Experiencing chest pain is scary. It often brings immediate worry. Is it my heart? This thought is common. Acute pain needs urgent attention. Call emergency services right away. But sometimes pain lingers. It becomes a chronic issue. This chronic pain needs investigation. It’s important not to ignore it. Your health is worth exploring.
Causes and Treatments for Chronic Chest Pain
Chronic chest pain has many causes. It’s not always heart-related. Understanding the source is key. Proper treatment depends on this. It requires thorough evaluation. A doctor’s expertise is vital. Don’t self-diagnose symptoms. Seek professional medical advice. Relief is often possible. Many effective treatments exist. Take control of your health.
Understanding Chronic vs. Acute Pain
Acute chest pain is sudden. It’s often sharp and severe. It needs immediate medical help. Chronic chest pain is different. It lasts for weeks or months. It might be constant or intermittent. Its intensity can vary daily. It’s not always a medical emergency. But it demands careful attention. Don’t confuse the two types.
Cardiac Causes of Chest Pain
Heart issues can cause chronic pain. Angina is a common culprit. It’s chest pain from reduced blood flow. Coronary artery disease causes it. Microvascular angina is also possible. Spasms in heart arteries too. Pericarditis causes sharp pain. It’s inflammation of the heart sac. Myocarditis is heart muscle inflammation. These need careful cardiac review.
Gastrointestinal System Issues
Your digestive system can cause pain. Acid reflux is a common one. Stomach acid backs up. It irritates the esophagus. This feels like burning chest pain. Esophageal spasms mimic heart attacks. Swallowing disorders can also contribute. Peptic ulcers may cause discomfort. Gallbladder problems might radiate. These are often mistaken for heart issues.
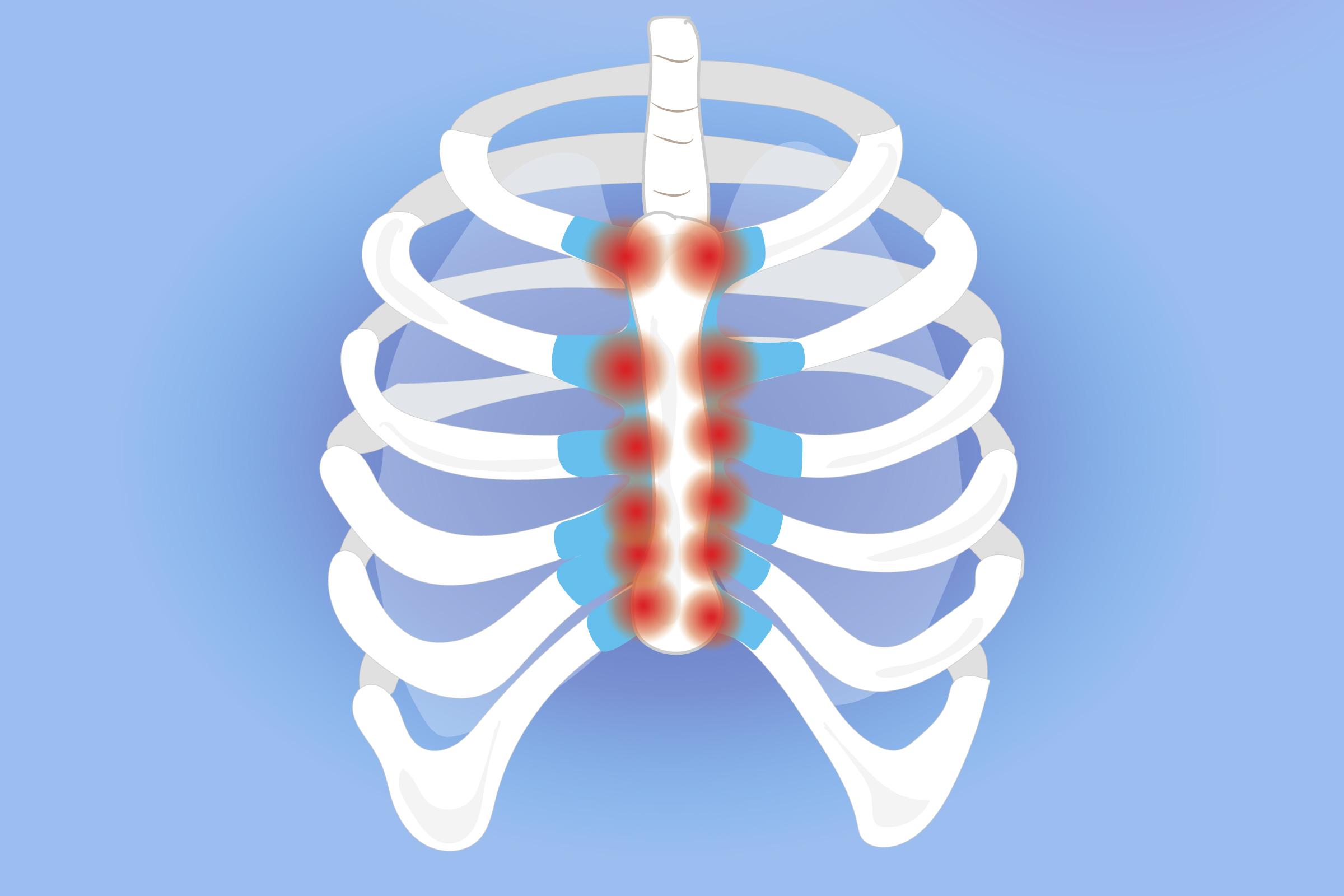
Musculoskeletal Sources
Pain from muscles or bones is common. Costochondritis is breastbone pain. It’s cartilage inflammation in ribs. Rib fractures cause sharp pain. Muscle strains can linger. Postural issues contribute sometimes. Arthritis in the spine might radiate. Fibromyalgia causes widespread pain. These often worsen with movement. Pressing on the chest helps diagnosis.
Pulmonary System Concerns
Lung conditions can cause pain. Pleurisy is lung lining inflammation. It hurts with deep breaths or coughs. Asthma can cause chest tightness. Chronic bronchitis may cause discomfort. Pulmonary hypertension also causes pain. Blood clots in lungs are serious. These are called pulmonary embolisms. Lung cancer can cause persistent pain. Breathing issues are often present.
Neuropathic and Nerve Pain
Nerve damage causes pain. Shingles can cause post-herpetic neuralgia. This affects nerves after an infection. Pinched nerves in the spine. They might radiate to the chest. Neuropathic pain is often burning. It can be sharp or tingling. Diagnosing nerve pain is tricky. It needs careful neurological assessment. Treatment targets nerve signals.
Psychological and Stress Factors
Mental health impacts pain. Anxiety attacks mimic heart attacks. Panic disorder causes chest tightness. Stress exacerbates physical symptoms. Depression can lower pain tolerance. Somatic symptoms are physical manifestations. Addressing mental health helps. Therapy and medication can assist. Don’t underestimate this link. Your mind affects your body.
Diagnosis: A Detailed Approach
Diagnosis is a careful process. Your doctor takes a full history. They ask about pain characteristics. A physical exam is performed. Blood tests might be ordered. ECG checks heart rhythm. Stress tests assess heart function. Endoscopy looks at esophagus/stomach. Imaging like X-rays or CT scans. These pinpoint the exact cause. It’s a systematic investigation.
Medical Treatments for Chronic Pain
Treatment depends on the cause. Heart issues get specific drugs. Acid reflux uses antacids. Muscle pain might need NSAIDs. Nerve pain gets special medications. Antidepressants can help chronic pain. Your doctor tailors treatment. It addresses the underlying problem. Medications manage symptoms too. It’s often a multi-pronged approach.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Care
Lifestyle changes often help. A healthy diet is important. Regular exercise, if tolerated. Stress reduction techniques are vital. Quitting smoking is paramount. Limiting alcohol helps greatly. Avoiding trigger foods for reflux. Hot or cold packs for muscle pain. These offer additional relief. Your daily habits matter.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy can be effective. It strengthens weak muscles. It improves posture and flexibility. It reduces muscle tension. Manual therapy might be used. They teach pain coping strategies. Rehabilitation helps restore function. It’s especially useful for musculoskeletal pain. Follow their guidance carefully. Consistency brings good results.
When to Seek Specialist Care
Sometimes, specialists are needed. A cardiologist for heart issues. A gastroenterologist for GI problems. A pulmonologist for lung conditions. A neurologist for nerve pain. A pain management specialist helps too. They offer advanced therapies. Don’t hesitate to ask for referrals. Complex cases need experts. Getting the right care matters.
